Understanding Medical Instruments: Essential Tools for Modern Healthcare
The field of medicine is constantly evolving, and at the core of this evolution are medical instruments. These tools are vital for healthcare professionals, allowing them to diagnose, treat, and manage a wide range of health conditions effectively. This article will delve into the various types of medical instruments, their significance, and how they contribute to enhancing patient care.
What Are Medical Instruments?
Medical instruments refer to a wide range of tools and devices that are used in the healthcare field. They can range from simple tools like stethoscopes to complex machines like MRI scanners. Their primary purpose is to assist healthcare professionals in diagnosing, monitoring, and treating patients efficiently and accurately.
The Importance of Medical Instruments in Healthcare
Medical instruments play a crucial role in the healthcare system. Here are several reasons why they are indispensable:
- Accurate Diagnosis: Medical instruments enable doctors to diagnose conditions accurately and quickly. For example, imaging devices like X-rays and CT scans provide detailed views of the body's internal structures.
- Effective Treatment: Instruments like surgical tools and infusion pumps are essential for performing procedures and delivering treatment effectively.
- Patient Monitoring: Monitoring devices, such as ECG machines and glucose monitors, help healthcare providers track a patient's condition in real time.
- Enhancing Safety: Many modern medical instruments are designed with safety features that reduce the risk of complications during procedures.
Types of Medical Instruments
Medical instruments can be categorized into several types based on their application and functionality. Below are some of the primary categories:
1. Diagnostic Instruments
These instruments are essential for diagnosing various medical conditions. Examples include:
- Stethoscope: Used to listen to heartbeats, breath sounds, and other bodily sounds.
- Sphygmomanometer: Measures blood pressure.
- Otoscope: Allows physicians to examine the ears.
- Endoscope: A tool used to view the gastrointestinal tract.
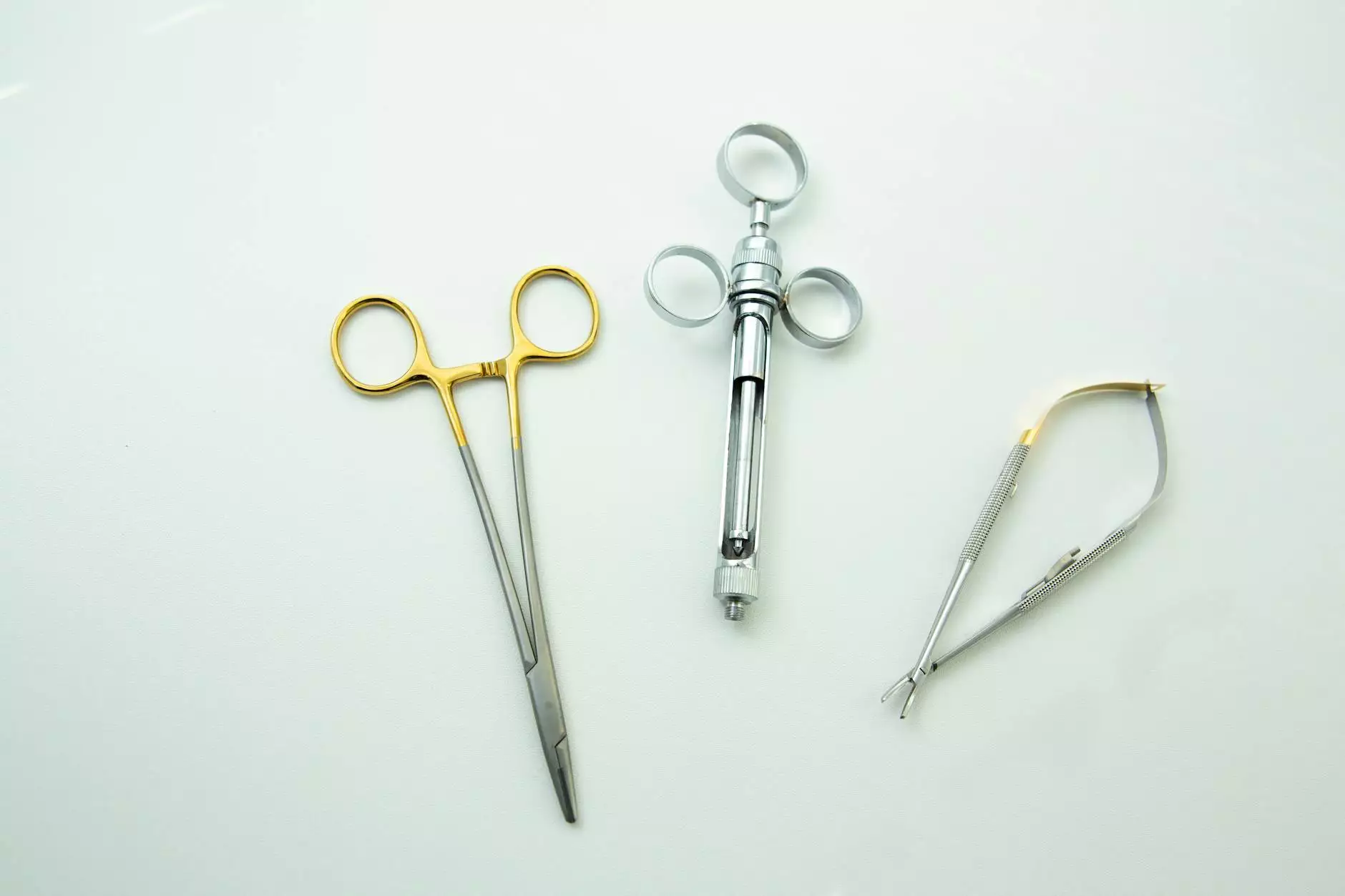
2. Surgical Instruments
Surgical instruments are designed specifically for use in surgical procedures. Key examples include:
- Scalpel: A small knife used for incisions.
- Scissors: Used for cutting tissues.
- Forceps: Handy for gripping and manipulating tissues.
- Suction devices: Helps to remove fluid from the surgical site.
3. Therapeutic Instruments
These instruments aid in the treatment of medical conditions. Some of them are:
- Infusion Pumps: Used to deliver fluids and medications to patients.
- Physiotherapy Equipment: Tools designed to assist in rehabilitation and physical therapy.
4. Monitoring Instruments
Monitoring instruments are essential for checking a patient's vital signs and health status. Notable examples include:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): Monitors heart activity.
- Pulse Oximeter: Measures oxygen saturation in the blood.
- Blood Glucose Monitor: Used by diabetic patients to check blood sugar levels.
Advancements in Medical Instruments
The healthcare industry is continually advancing, particularly in the field of medical instruments. Here are a few notable trends:
1. Technological Integration
The integration of technology into medical instruments has revolutionized healthcare. Instruments now often feature:
- Digital Displays: Providing real-time data and improving clarity.
- Wireless Connectivity: Allowing for instant sharing of patient data with healthcare providers.
- Telemedicine Capabilities: Some instruments are now designed to be used remotely, facilitating patient care from a distance.
2. Improved Ergonomics
Modern medical instruments are designed with ergonomics in mind, ensuring comfort for healthcare providers during use. This focus on ergonomics leads to:
- Reduced Fatigue: Instruments are lighter and easier to handle, minimizing strain.
- Enhanced Precision: Improved designs allow for more accurate manipulation and control during procedures.
3. Enhanced Sterilization Techniques
Infection control is critical in healthcare, and advancements in sterilization techniques have greatly improved patient safety. Use of:
- Antimicrobial Materials: Many instruments are now made with materials that resist bacterial growth.
- Automated Sterilizers: These devices ensure that instruments are thoroughly disinfected before use.
Challenges in the Use of Medical Instruments
While the benefits of medical instruments are vast, there are also challenges that healthcare providers must navigate:
1. Cost
The cost of acquiring and maintaining modern medical instruments can be high. Healthcare facilities must balance quality with affordability to ensure they can provide the best care while managing budgets effectively.
2. Training and Familiarization
As instruments become more advanced, healthcare professionals must undergo extensive training to effectively use them. Ensuring that all staff members are proficient with new tools is essential for maximizing their benefits.
3. Maintenance and Calibration
Regular maintenance and calibration of medical instruments are crucial to ensure their accuracy and functionality over time. This requires dedicated personnel and financial investment.
The Future of Medical Instruments
The future of medical instruments looks bright, with numerous innovations on the horizon. As technology continues to advance, we can expect:
- Artificial Intelligence Integration: AI-driven tools that assist in diagnostics and treatment planning will likely become commonplace.
- Personalized Medical Instruments: Instruments tailored to individual patient needs will enhance care quality.
- Improved Telehealth Solutions: Expect more advanced instruments that facilitate remote patient monitoring and consultations.
Conclusion: The Indispensable Role of Medical Instruments
In conclusion, medical instruments are a cornerstone of modern healthcare, enabling accurate diagnoses, effective treatments, and efficient patient monitoring. Their importance cannot be overstated as they not only save lives but also enhance the quality of care provided by healthcare professionals across various settings, including medical centers.
The future holds exciting possibilities for the development and usage of these instruments, driven by technological advancements and the continuous pursuit of better healthcare solutions.