The Art of Architectural Maquettes: Crafting Vision Into Reality
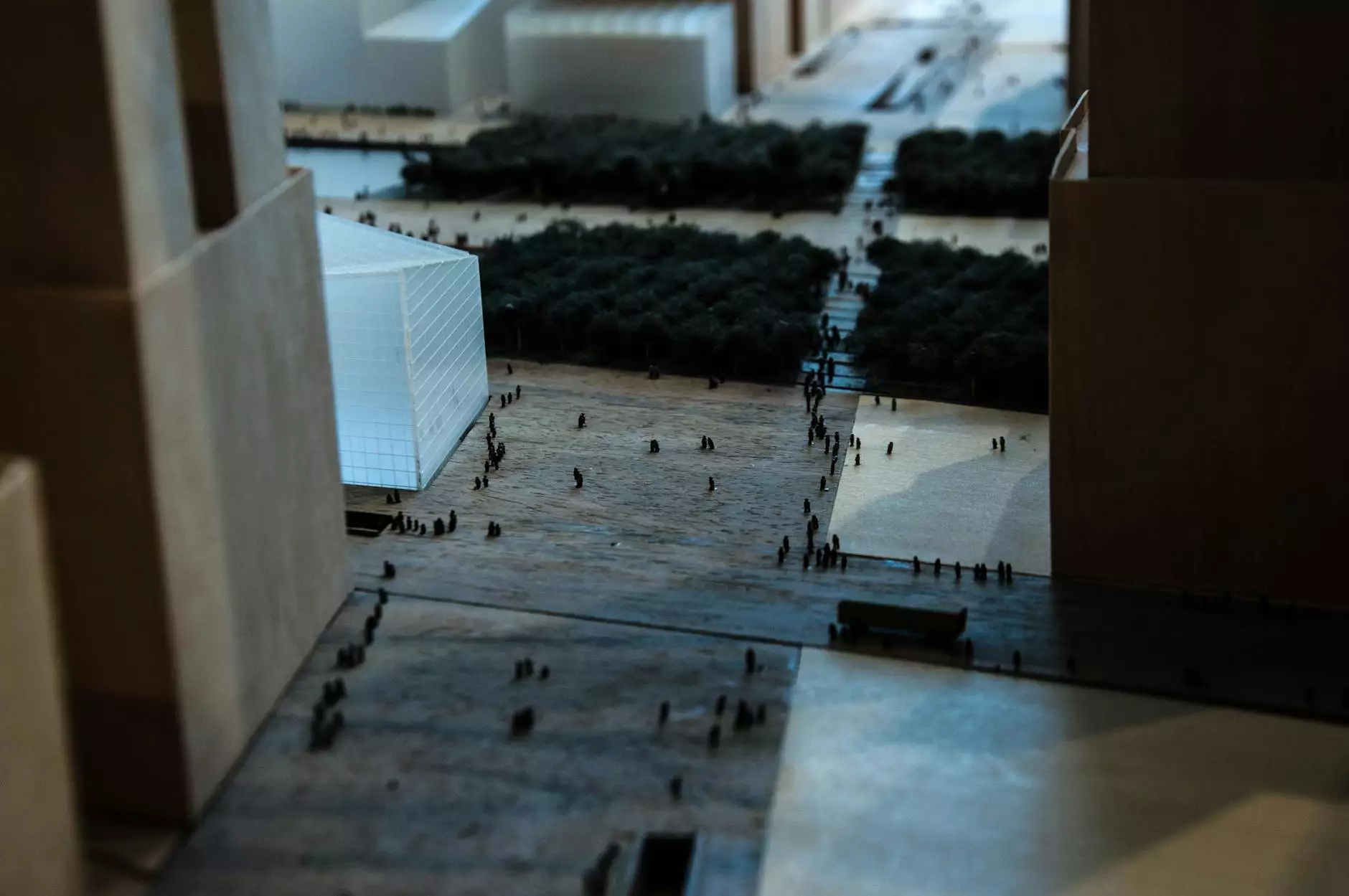

In the world of architecture, the translation of ideas into reality is paramount. One of the most effective methods of achieving this transformation is through architectural maquettes. These intricate scale models serve as powerful tools for architects and designers, providing a tangible representation of their creative visions. In this article, we will explore the significance of architectural maquettes, the process of their creation, their impact on architectural projects, and best practices for their effective utilization.
Understanding Architectural Maquettes
An architectural maquette is a three-dimensional scale model created to represent an architectural design concisely. The term "maquette" is derived from the French word for "model", indicating an artistic approach to representation. These models can vary in size, complexity, and materials, but they share a common purpose: to visually communicate the form and function of a proposed design.
The Importance of Architectural Maquettes
Architectural maquettes play several critical roles in the architectural design process:
- Visualization: They help clients and stakeholders visualize the project, turning abstract plans and drawings into a more comprehensible format.
- Communication: Maquettes serve as communication tools between architects, clients, and other professionals, ensuring everyone has a clear understanding of the project.
- Design Exploration: Creating a physical model allows architects to explore and manipulate designs in a tangible way, facilitating creativity and innovation.
- Physical Context: Maquettes can be placed in real environments, providing valuable insights into how the design interacts with its surroundings.
The Process of Creating Architectural Maquettes
The journey of creating an architectural maquette is both an art and a science. Below are the essential steps involved in crafting these detailed models:
1. Concept Development
The first step in creating an architectural maquette involves developing the design concept. This phase requires thorough research and collaboration among architects, clients, and stakeholders. Key elements to consider during this stage include:
- Client Needs: Understanding what the client wants and needs from the design.
- Site Analysis: Evaluating the feasibility of the project in the intended location.
- Aesthetic Vision: Defining the desired aesthetic qualities of the space.
2. Material Selection
The choice of materials is crucial in creating an effective architectural maquette. Common materials include:
- Cardboard: Lightweight and easy to manipulate.
- Foam Board: Offers a smooth surface and can be easily cut into shapes.
- Wood: Provides durability and a sturdy feel.
- Plastic: Ideal for high-detail models.
Choosing the right materials not only affects the model's appearance but also influences its scale and durability.
3. Scale and Measurement
Choosing an appropriate scale is vital in accurately representing the building's proportions. Common scales for architectural maquettes include:
- 1:50: A popular scale for detailed views of buildings.
- 1:100: Useful for larger projects where details can be simplified.
- 1:200: Often used for urban planning and larger developments.
4. Construction Techniques
Once the concept is developed and the materials selected, the actual construction of the maquette begins. Techniques used can include:
- Cutting: Using sharp tools to create precise shapes.
- Gluing: Adhering elements together securely for stability.
- Painting: Adding coloration and texture to enhance realism.
- Assembly: Bringing together all components into a cohesive model.
Attention to detail in this phase is crucial, as even minor inaccuracies can lead to misrepresentation.
Impact of Architectural Maquettes on Project Success
The utilization of architectural maquettes can significantly impact the trajectory of a project. Here's how:
Client Approval
Having a tangible representation of a project can greatly increase the likelihood of client approval. A well-crafted maquette allows clients to envision the final product, providing them with a sense of involvement and satisfaction. This visual tool can lead to quicker decisions and consensus, streamlining the approval process.
Enhanced Collaboration
Architectural maquettes foster collaboration among architects, engineers, and contractors. By providing a shared reference point, all parties can easily communicate ideas and critiques, leading to a more refined project outcome. This collaborative environment can encourage innovation and creativity, resulting in unique architectural solutions.
Marketing and Presentation
For architecture firms, architectural maquettes serve as powerful marketing tools. They can be used in presentations to potential clients or showcased at industry events to attract interest. A stunning maquette can effectively captivate and engage audiences, setting a firm apart from its competitors.
Best Practices for Utilizing Architectural Maquettes
To maximize the effectiveness of architectural maquettes, consider these best practices:
1. Keep It Simple
While detail is important, overly complex maquettes can overwhelm viewers. Aim for a balance that highlights key features without unnecessary intricacies.
2. Choose the Right Scale for the Audience
Tailor the scale of the maquette according to the audience. For client presentations, a larger scale might be necessary to highlight specific elements, while smaller scales may be suitable for general overview presentations.
3. Use Quality Materials
Invest in quality materials that can withstand handling and transport. High-quality materials not only enhance the aesthetic but also convey professionalism and attention to detail.
4. Integrate Contextual Elements
Incorporating surrounding context such as landscapes, roads, and existing structures can provide a more complete understanding of how the design fits into its environment. This practice enhances the realism of the model.
5. Seek Feedback
Before finalizing the maquette, seek feedback from colleagues and stakeholders. This collaborative review process can uncover areas for improvement and lead to a stronger final presentation.
The Future of Architectural Maquettes
As technology advances, the future of architectural maquettes is evolving. Digital tools and 3D printing are increasingly being used to create more sophisticated models. Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) also present exciting new avenues for architectural visualization, enhancing how architects and clients interact with designs. However, the traditional physical maquette continues to hold a unique place in the architectural process, blending craftsmanship with design.
Conclusion
In summary, architectural maquettes are invaluable tools in the field of architecture, offering a myriad of benefits from enhancing visualization to facilitating collaboration. They serve not only as models but as integral components of the architectural process that bridge the gap between conceptualization and realization. By investing time and resources into creating high-quality models, architects can significantly influence the success of their projects and deepen the engagement of their clients. The art of architectural maquettes is a blend of creativity, precision, and purpose, paving the way for innovative architectural endeavors in the future.